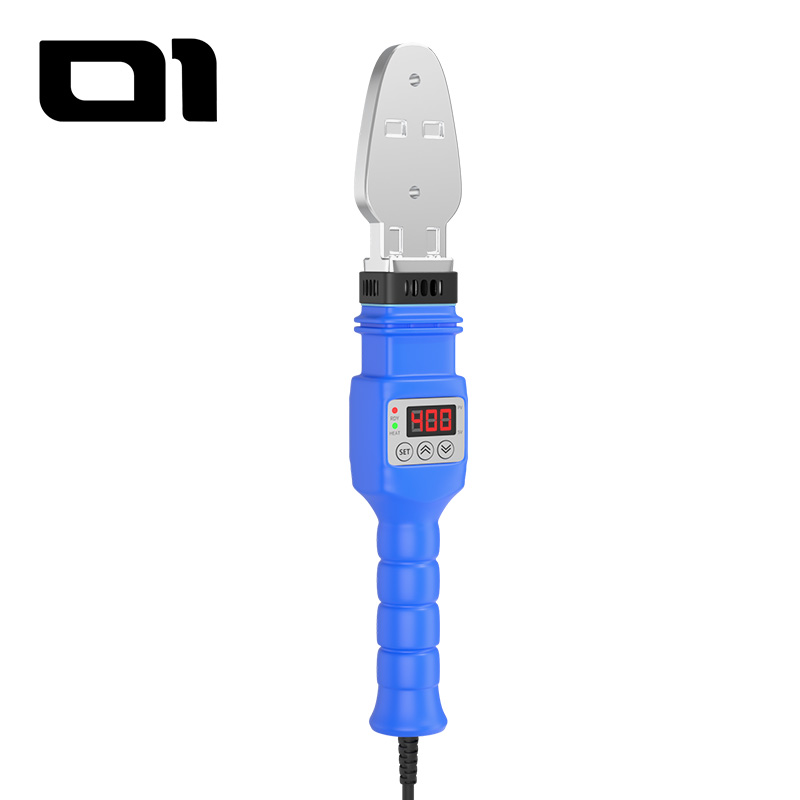
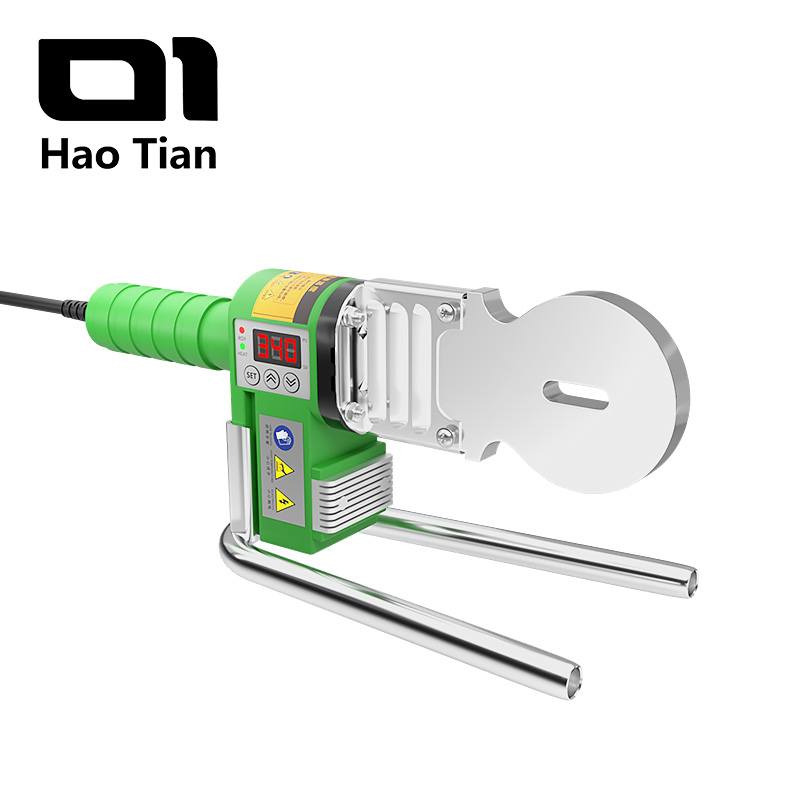
Welding PPR pipes in winter requires special attention. Low temperatures make the fusion process more complex and can affect the strength of the joint.
Understanding the challenges of cold-weather welding is essential. PPR pipes can become brittle in low temperatures, increasing the risk of cracking and causing fusion defects.
Proper preparation and machine setup are critical. The fusion welder must provide accurate and stable temperature control to ensure consistent results. Safety is equally important—using protective gear reduces the risk of accidents and ensures a safe working environment.
1. Understanding PPR Pipes and Their Cold-Weather Challenges
PPR pipes are widely used in plumbing and heating systems due to their durability and high-temperature resistance. However, cold environments can negatively impact material performance and increase welding difficulty.
When temperatures drop, PPR becomes more brittle. This raises the likelihood of cracks during socket fusion or alignment. Knowing how temperature affects PPR is crucial for quality assurance.
Key cold-weather challenges include:
- Increased brittleness of PPR pipes
- Higher risk of welding failure
- Difficulty in retaining sufficient heat during fusion
Addressing these challenges requires material awareness and proper preparation.
2. Preparation Before Winter Welding
Preparation is the key to successful winter welding of PPR pipes. Before starting the job, evaluate the environmental conditions—especially ambient temperature and humidity—as both factors directly impact the fusion process.
Pipe storage is often overlooked. Before welding, store PPR pipes and fittings in a warm, sheltered area. Cold pipes are more likely to crack, and fusion performance may suffer.
Preheating the pipes slightly before welding is also beneficial. Proper preheating reduces brittleness and helps achieve complete fusion.
Creating a controlled working environment improves welding quality. Consider the following methods:
- Use covers or barriers to block wind and moisture
- Place portable heaters nearby to maintain a stable temperature
- Monitor and adjust ambient conditions throughout the operation
These preparation steps help mitigate the negative effects of cold temperatures.
Safety tips for PPR welding machines
3. Professional Fusion Welding Machine Setup for Winter Conditions
equipment performance in low temperatures is one of the most critical factors affecting weld quality. Winter conditions demand higher standards for temperature stability, insulation performance, electrical safety, and mechanical durability. A well-designed fusion welder can significantly reduce the risk of brittle fractures, incomplete melting, temperature loss, and joint failure.
Use Fusion Welders Designed for Low-Temperature Environments
Not all machines can operate reliably in winter. Professional-grade welders should include:
- Digital temperature control with ±1–2°C precision
- Fast heat recovery system to compensate for ambient temperature loss
- Thickened heating plates for superior heat retention
- High-density brass or aluminum alloy welding dies
- Intelligent thermostat or sensor-based regulation
These designs prevent temperature drop during socket insertion and welding cycles.
Increase Welding Temperature by 10–20°C
In freezing environments, heat dissipates faster. To balance this effect:
- Set the fusion temperature 10–20°C higher than standard values
- Allow the machine to reach full temperature before operation
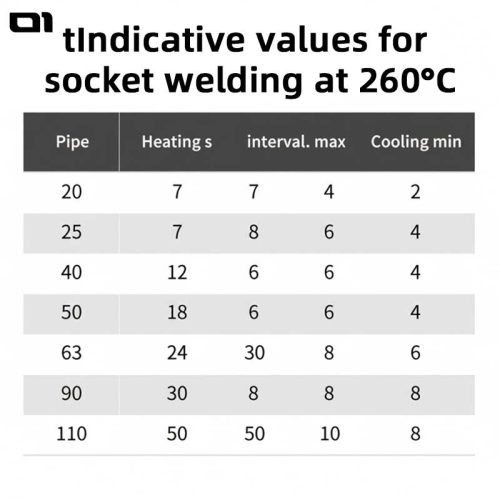
- Follow cold-weather welding time and pressure specifications
This ensures sufficient molecular bonding during fusion.
Use Thickened Heating Dies and Plates
For winter applications, recommend or supply:
- Thicker socket dies to improve insulation
- Reinforced heating plates with better thermal mass
These upgrades are especially important for outdoor plumbing, construction, and municipal installations.
Power Cable Must Be Winter-Resistant
Cold temperatures affect not only the fusible materials but also the electrical components. To ensure safe and stable operation, the power cable must meet winter standards:
- Use thickened rubber or TPE cold-resistant insulation
- Prevent cable hardening, cracking, or loss of flexibility below 0°C
- Ensure sheath material remains pliable at -10°C to -20°C
- Protect the cable from ice, snow, and water ingress
- Avoid PVC-only cables, which become brittle in winter
For extreme outdoor environments, it is recommended to use industrial-grade antifreeze cables or add insulation sleeves to existing power cords.
Maintenance and Pre-Use Inspection
Before winter welding:
- Test temperature sensors and heating elements
- Inspect cables and plugs for stiffening or surface cracks
- Check controller accuracy and voltage stability
- Remove frost or moisture from machine surfaces
Preventive checks reduce breakdown rates and improve temperature consistency.
Proper Machine Placement
Even the best machine loses heat quickly in exposed conditions. Recommend:
- Keep the welding machine in a wind-protected or semi-enclosed area
- Use thermal covers or wind guards
- Avoid placing it directly on frozen ground or wet surfaces
Stable placement improves fusion consistency and reduces heat loss.
4. Best Practices for Welding PPR Pipes in Low Temperatures
Cold-weather welding requires a strategic approach to prevent defects. Before fusion, preheat the pipe surface slightly. This reduces brittleness and improves socket connection quality.
Perform welding in a sheltered or enclosed space whenever possible. Avoid exposure to wind, humidity, or snow, as these factors disrupt the heating cycle. Insulated tents, enclosures, or windbreaks can maintain a more stable temperature.
Adjust the fusion time according to the environment. Lower temperatures often require slightly longer heating and cooling durations to achieve full bonding.
Checklist for smoother performance:
- Preheat pipes before fusion
- Choose a sheltered, stable working area
- Adjust heating and cooling times for cold-weather conditions
5. Post-Welding Inspection and Quality Assurance
After welding, thorough inspection is essential. Cold weather can compromise the structural integrity of joints.
Inspect the weld seam for signs of weakness or defects, such as cracks, deformation, or incomplete bonding. Early detection prevents major system failures.
Follow a quality assurance checklist to verify results:
- Look for cracks or visible defects
- Confirm full fusion and proper alignment
- Conduct pressure testing to verify strength
Keep inspection records as reference for future maintenance. Careful evaluation ensures long-term joint reliability, regardless of weather conditions.
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid During Winter Welding
Winter creates unique welding challenges, and avoiding typical mistakes is critical. A common oversight is ignoring the brittle characteristics of PPR in cold weather. Brittle pipes crack easily, resulting in poor welds.
Another mistake is failing to adjust the fusion machine. Without increasing the temperature or fusion time, cold-weather welding often fails to bond correctly.
Key mistakes to avoid:
- Ignoring increased pipe brittleness
- Skipping machine temperature adjustments
- Failing to preheat pipes when necessary
By staying alert and informed, installers can reduce costly failures and maintain system integrity.
7. Conclusion & Expert Recommendations
Welding PPR pipes in winter requires more than standard operating steps. Low temperatures affect not only the fusion process but also the long-term performance of the installed pipeline system. Proper preparation, accurate temperature control, and adherence to cold-weather parameters are essential to ensure strong and durable joints.
- Thorough equipment checks before winter operation
- Use of controlled or sheltered welding environments to avoid temperature loss
- Adjustment of fusion temperature and time according to ambient conditions
- On-site training or guidance for cold-weather welding practices
- Strict compliance with manufacturer specifications on fusion depth, heating duration, and cooling time
Post-Installation Protection Is Critical
For pipelines installed outdoors or in environments where temperatures may drop below freezing, we strongly recommend applying post-installation insulation and anti-freeze wrapping to the pipes after welding is completed. This helps to:
- Prevent PPR pipes from becoming brittle and cracking in freezing temperatures
- Avoid water expansion inside the pipe that may lead to rupture
- Reduce the risk of secondary repairs or system downtime
- Extend service life and maintain pressure integrity in winter conditions
Insulation materials such as foam sleeves, rock wool, rubber insulation tubes, or thermal protective wraps should be applied depending on the installation environment and exposure level.
Taking preventive insulation measures after installation is as important as ensuring welding quality. This proactive approach minimizes maintenance costs and protects the entire system from winter-related failures.