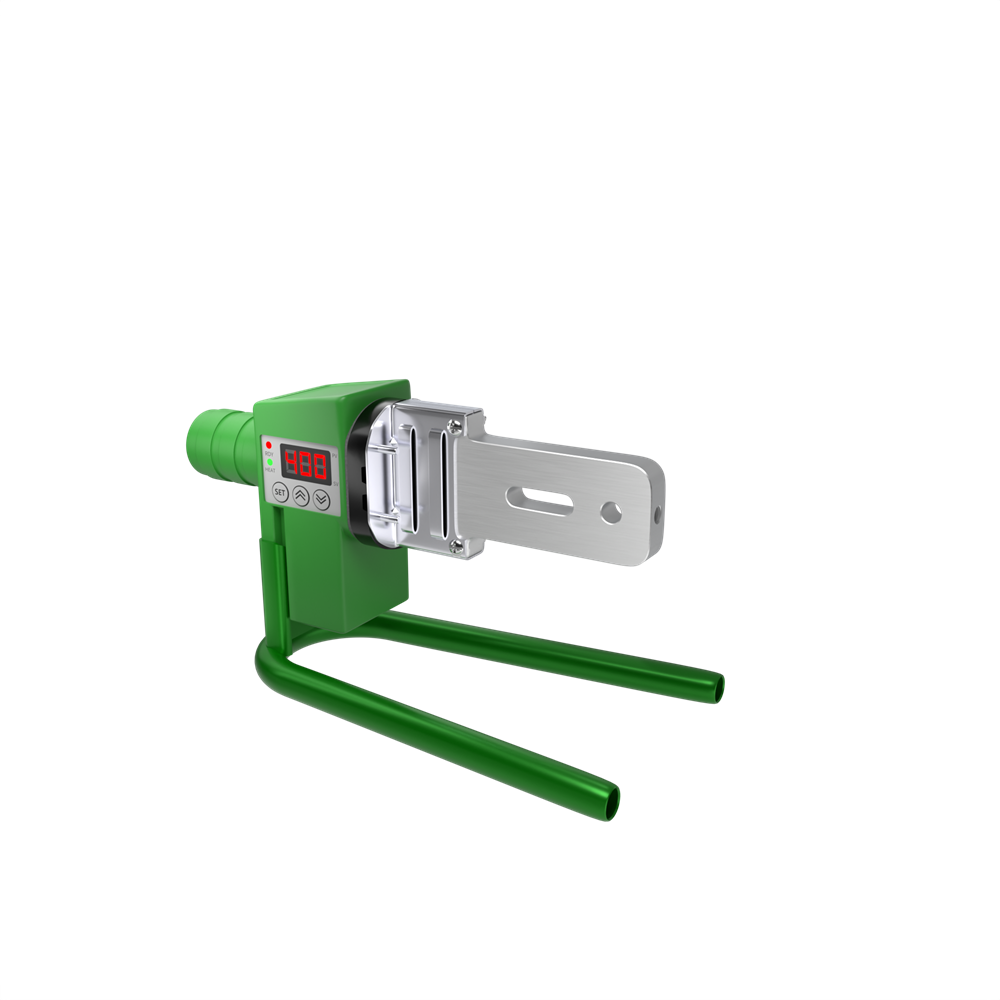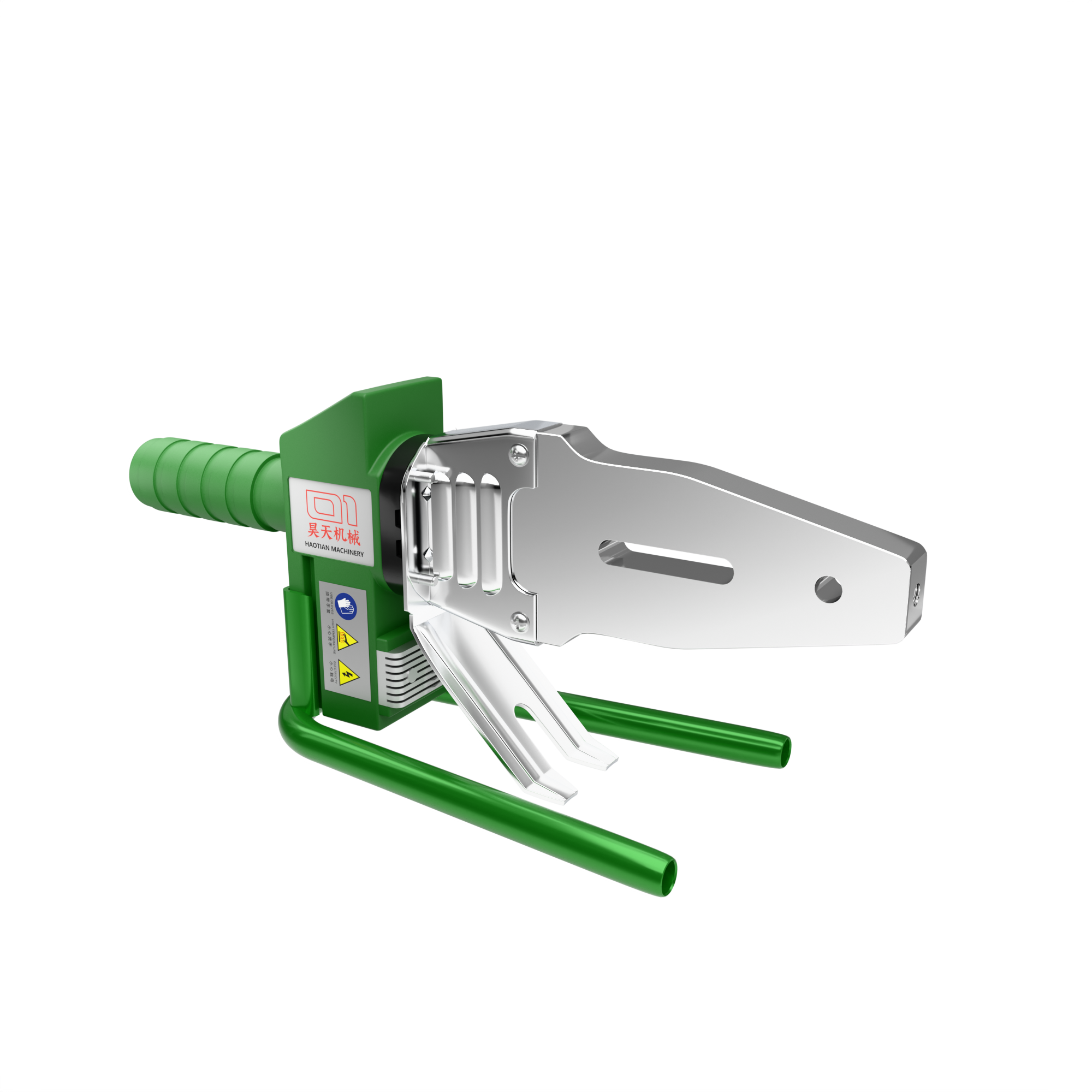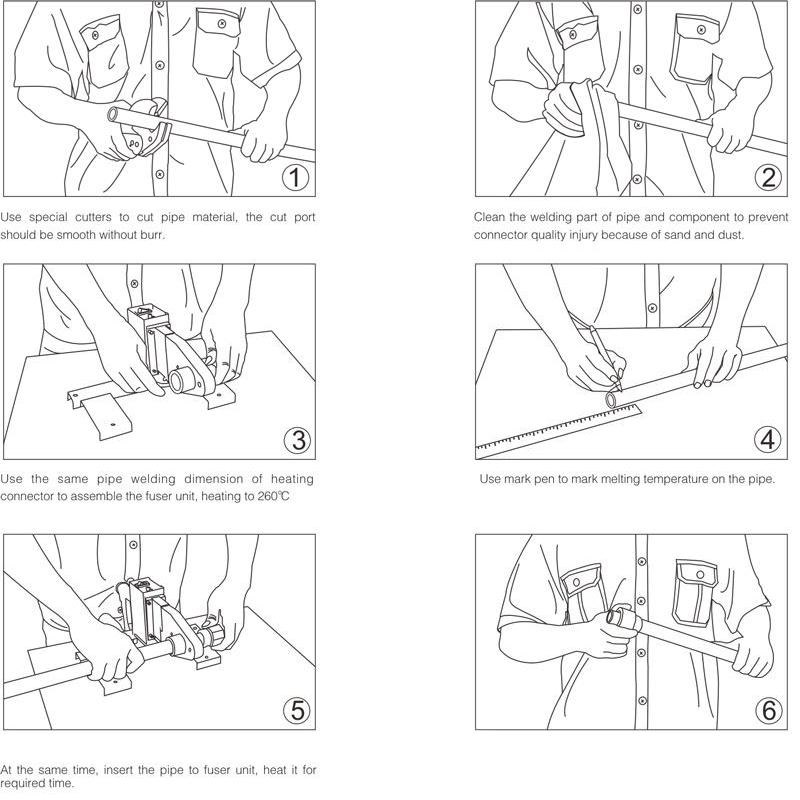
The safety and service life of PPR piping systems depend critically on fusion welding quality. Mastery of the following operational essentials is imperative:
- Precise Temperature Control (260℃±10)
Meikang Piping Industry engineers warn: Adjustable fusion welders (PPR/PE dual-use, as shown below) pose significant risks due to temperature inaccuracy—- Overheating → Excessive liquefaction → Pipe end constriction (ID reduction ≥30%)
- Underheating → Incomplete fusion → Cold-joint delamination (70% higher leakage risk)
Conclusion: Strongly discourage using adjustable welders for PPR connections.
- Standardized Welding Depth
- Excessive depth: Material overflow → Flow path constriction
- Insufficient depth: Inadequate bonding → Pressure-bearing failure
Protocol: Follow depth standards by diameter (e.g., DN20 pipe=14.5±0.5mm)
- Accurate Heating DurationDiameter(mm)Heating(s)Tolerance205±0.5257±0.5328±0.5Overtime effect: Melt flow index surge → Constriction exceeding GB/T 18742.3 limit (≤5%)
- Jointing Procedure
- Push aligned along horizontal axis (Speed ≤3mm/s)
- Pressure maintenance ≥5 seconds (Rotation PROHIBITED! Causes molecular chain disorientation)
Final Quality Assurance:
All welded systems must undergo hydrostatic testing (Test pressure=1.5×working pressure, duration ≥30 min) to eliminate micro-leakage defects.