In today’s plumbing industry, welding is no longer a specialized niche skill—it has become a core competency that determines a plumber’s professional value, project adaptability, and long-term success. Whether working on residential installations, commercial systems, municipal pipelines, or industrial facilities, plumbers are expected to deliver joints that are durable, leak-free, and compliant with safety and pressure standards. Among the many pipe materials used across the world, PPR (Polypropylene Random Copolymer) pipes have become the dominant choice, making PPR welding an essential ability every plumber must master.
While tools such as fusion welding machines, socket welders, and butt fusion systems assist in achieving strong pipe joints, the true capability still depends on the plumber’s understanding of techniques, preparation, temperature control, and inspection. A skilled plumber doesn’t just “use a welding machine”—they understand why, when, and how to apply the correct welding method for each material and installation environment.
1. Why Welding Skills Define Today’s Plumbers
In plumbing, welding is not simply joining pipes—it is the foundation of pipeline safety, performance, and longevity. As building codes and customer expectations evolve, plumbers who can perform strong, reliable welds gain a clear edge over those limited to mechanical or adhesive connections.
Welding is essential because:
- It ensures leak-free, long-term performance
- It supports pressure-bearing systems
- It enables custom installations and on-site adjustments
- It reduces failure rates in hot water, heating, industrial, and irrigation projects
- It increases a plumber’s ability to work across multiple materials
With the industry-wide adoption of PPR pipes—now standard in Europe, Asia, the Middle East, South America, and expanding in North America—PPR fusion welding has become a core must-have skill. Even plumbers skilled in metal pipe welding must now master plastic pipe fusion to remain competitive.
2. PPR Welding as a Core Competency in Modern Plumbing
PPR pipes are widely used due to their high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, low maintenance requirements, and suitability for hot and cold water systems. As a result, plumbers who cannot weld PPR properly will face increasing limitations in both residential and commercial work.
Why every plumber must master PPR welding:
- PPR dominates new construction and renovation projects
- Fewer leaks compared to threaded or glued pipe systems
- Fusion joints offer seamless internal flow and long-term durability
- Ideal for pressure-bearing systems and high-temperature applications
- Required in large-scale installations: schools, hotels, hospitals, etc.
While PPR fusion welding machines assist in making uniform joints, it’s the plumber’s manual precision—measuring depth, controlling angle, heating time, and cooling process—that determines whether the weld will hold under pressure
3. Core Welding Knowledge Every Plumber Should Have
Before mastering any pipe welding technique, there are foundational principles every plumber should understand:
3.1 Pipe Material Identification
- Plastic: PPR, PVC, CPVC, HDPE
- Metal: Copper, steel, stainless steel, brass
- Different materials require different welding approaches.
3.2 Heat, Pressure, and Fusion Principles
- Know how pipes melt and bond
- Understand temperature ranges (e.g., PPR: 250–280°C)
- Control fusion time and pressure during joining
3.3 Dimensions and Joint Integrity
- Wall thickness, diameter fit, socket vs butt joint compatibility
- Avoiding weak spots from misalignment or overheating
3.4 Application Environments
- Residential installations
- Commercial and industrial systems
- Municipal pipelines
- Repair and replacement jobs
A plumber who understands these fundamentals can weld PPR confidently and adapt techniques to PVC, HDPE, or metal pipes as needed.
4. Welding Methods Every Plumber Should Know
Even if PPR fusion is the most frequently used, well-rounded plumbers should master multiple welding methods to handle different materials and environments.
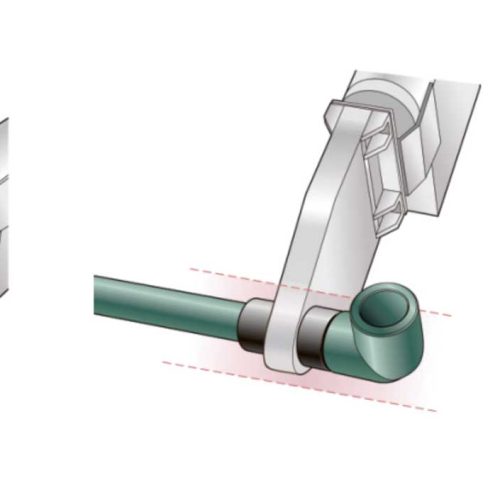
4.1 Socket Fusion Welding (Primary for PPR)
- Heat the pipe exterior and fitting interior
- Insert and hold for fusion
- Most common for 20–75mm PPR installations
4.2 Butt Fusion Welding
- Used for large-diameter PPR or HDPE pipes
- Pipe ends are heated, aligned, and pressed together
- Ideal for high-pressure systems
4.3 Electrofusion Welding
- Uses fittings with built-in heating elements
- Precise, clean, and suitable for tight spaces
- Popular in commercial and underground applications
4.4 Metal Pipe Welding (Arc / Gas / Brazing)
- Required for copper, steel, or stainless steel systems
- Critical in mixed-material projects and industrial plumbing
By knowing multiple welding types, plumbers become versatile, employable, and trusted for large contracts.
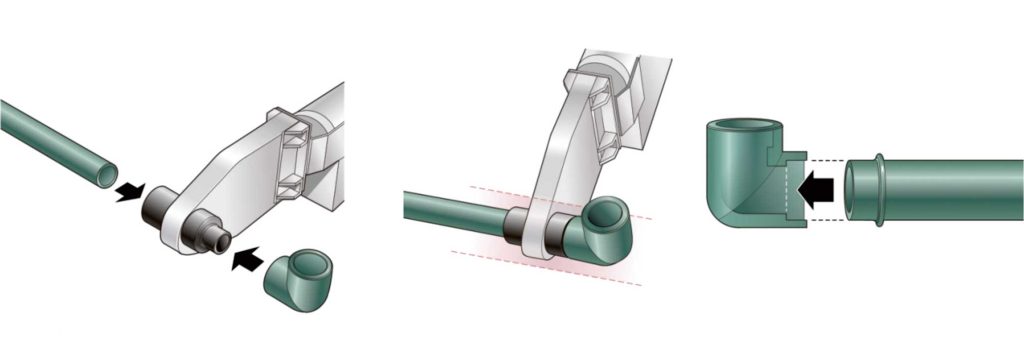
5. Step-by-Step PPR Welding: A Teaching-Based Guide
Although tools like handheld PPR welding machines support the process, the technique depends on the plumber, not the device. Below is a structured approach plumbers should follow:
Step 1: Cutting & Measuring
- Use a pipe cutter for clean, straight cuts
- Measure socket depth and mark alignment points
Step 2: Preparation & Cleaning
- Clean pipe ends and fittings
- Ensure no dust, water, grease, or burrs
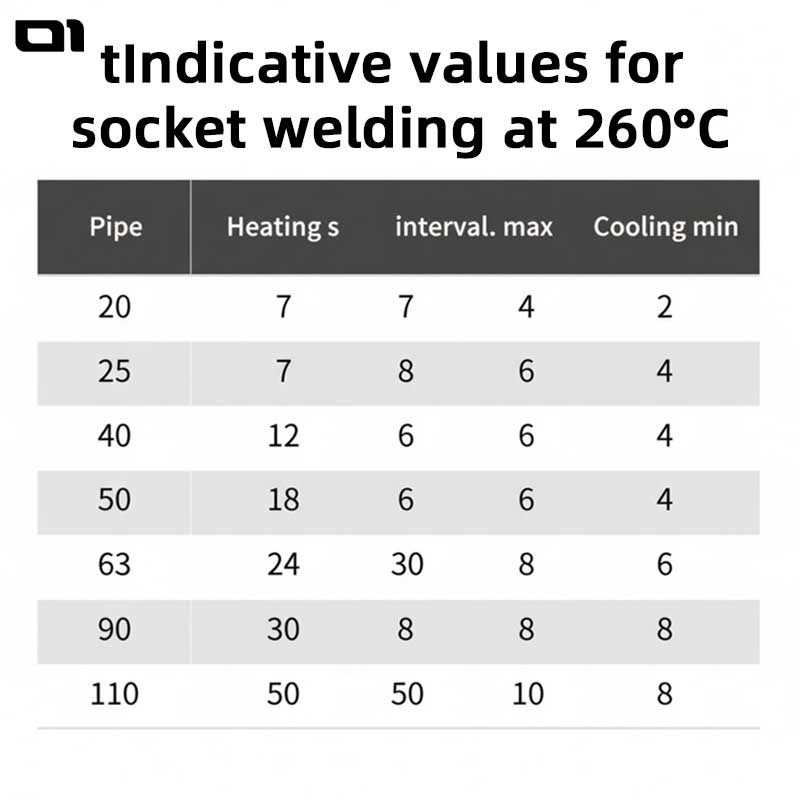
Step 3: Temperature Setting
- Typical fusion range: 250–280°C
- For digital fusion machines, ensure stable heat before welding
Step 4: Heating Phase
- Insert pipe and fitting into heating plate
- Hold for correct timing based on diameter
Step 5: Joint Fusion
- Quickly remove heated parts
- Insert pipe into fitting without rotation
- Maintain alignment and pressure
Step 6: Cooling & Stabilization
- Let the joint cool naturally—no force, water, or adjustment
- Cooling time is critical to final strength
This step-by-step approach ensures consistency and minimizes risk of leakage or joint failure.
6. Pipeline Pressure Testing: The Mark of Professionalism
Even perfect-looking welds must be pressure-tested to confirm reliability.
Why pressure testing matters:
- Detects hidden leaks and weak joints
- Ensures compliance with plumbing codes
- Builds customer trust and reduces callbacks
Standard Testing Process:
- Close valves and secure all joints
- Fill system with water or air
- Pressurize slowly to the required psi/bar
- Monitor pressure drop with a gauge
- Inspect visually for seepage
- If leaks appear, repair and retest
Plumbers who combine welding and pressure testing demonstrate complete system competency.
7. Common Welding Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced plumbers make errors that compromise quality. Recognizing and preventing these issues is a sign of mastery.
Mistake 1: Incorrect Temperature
Leads to weak bonding or material burn
Mistake 2: Misalignment
Causes stress cracks and future leaks
Mistake 3: Dirty Pipe Ends
Dirt or moisture blocks fusion
Mistake 4: Rushed Cooling
Weakens the joint structure
Mistake 5: Excessive Rotation
Destroys uniform bonding
Correcting these habits ensures long-term performance and fewer reworks.
8. Becoming a Welding-Capable Professional Plumber
The best plumbers don’t just “own a tool”—they command their technique. To grow in this field:
Develop Skills Beyond Tools
- Learn socket, butt, and electrofusion welding
- Understand pipe pressure ratings and code compliance
Combine Experience with Standards
- Master on-site problem solving
- Follow installation and safety guidelines
Upgrade Tools When Skills Improve
- A good welder with average tools > an untrained user with premium machines
Work With Multiple Pipe Types
- PPR as the base
- HDPE, PVC, copper, steel as extensions
Plumbers who integrate knowledge, technique, and adaptability become industry leaders.
9. Final Conclusion
Welding isn’t just another plumbing task—it’s the core of building durable, pressure-resistant, and leak-free systems. With PPR pipes dominating the modern plumbing market, PPR welding has transitioned from an optional specialty to a mandatory skill for serious professionals.
However, welding excellence is not defined by owning a fusion machine—it comes from:
- Understanding material behavior
- Applying correct heating and cooling techniques
- Performing precision cutting and alignment
- Testing every joint under pressure
- Avoiding common welding mistakes
By combining foundational welding knowledge with hands-on PPR fusion skills and the right supporting tools, plumbers can deliver reliable, code-compliant installations across all environments.
Whether you’re installing hot water systems, repairing commercial pipes, or handling new construction projects, mastering core welding skills gives you confidence, credibility, and career advantage.