Selecting the appropriate PPR pipe welding machine is essential for successful plumbing projects. Two common methods—butt welding and fusion welding—each offer distinct benefits and limitations. Understanding these differences helps in making an informed choice.
Butt welding involves heating pipe ends and pressing them together. It is often used for larger pipes and requires precision and skill. Fusion welding, also called socket fusion, melts the pipe and fitting surfaces using a heating element. It is more common for smaller pipes and is generally easier to use.
Both methods require specific machines to provide consistent heat and pressure. The decision between them depends on factors like pipe size, application, and user experience.
Understanding Butt Welding
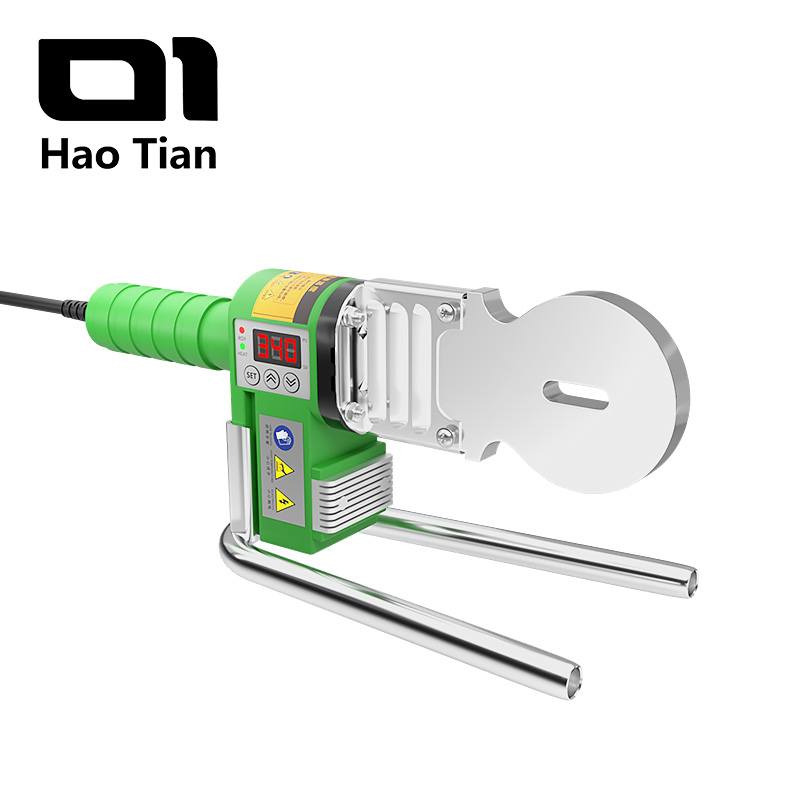
Butt welding is widely used in industrial applications for joining larger PPR pipes. The process involves heating the pipe ends until malleable and pressing them together to form a seamless joint.
Proper alignment and clean ends are critical to avoid weak joints. The machine heats the ends to a specific temperature based on material type and thickness. After heating, the ends are pressed together under pressure to form a strong bond. Cooling under pressure ensures a solid joint.
This method requires significant operator skill and sophisticated equipment. It is ideal for large-diameter pipes and thick-walled applications but involves higher costs and maintenance.
Key aspects of butt welding:
- Ideal for large diameters
- Provides strong, seamless joints
- Demands skilled operation
- High equipment cost
- Suited for industrial use
Advantages of Butt Welding
Butt welding offers robust, seamless joints with strength matching the pipe itself, making it suitable for high-pressure systems. It handles large diameters efficiently and ensures smooth fluid flow without internal obstructions. This reduces blockages and pressure loss. The joints are highly durable, minimizing long-term maintenance and repair costs.
Limitations of Butt Welding
The process requires skilled operators, adding time and cost for training. Equipment is expensive, and setup is time-consuming due to precise alignment needs. These factors can be challenging for smaller projects or limited budgets.
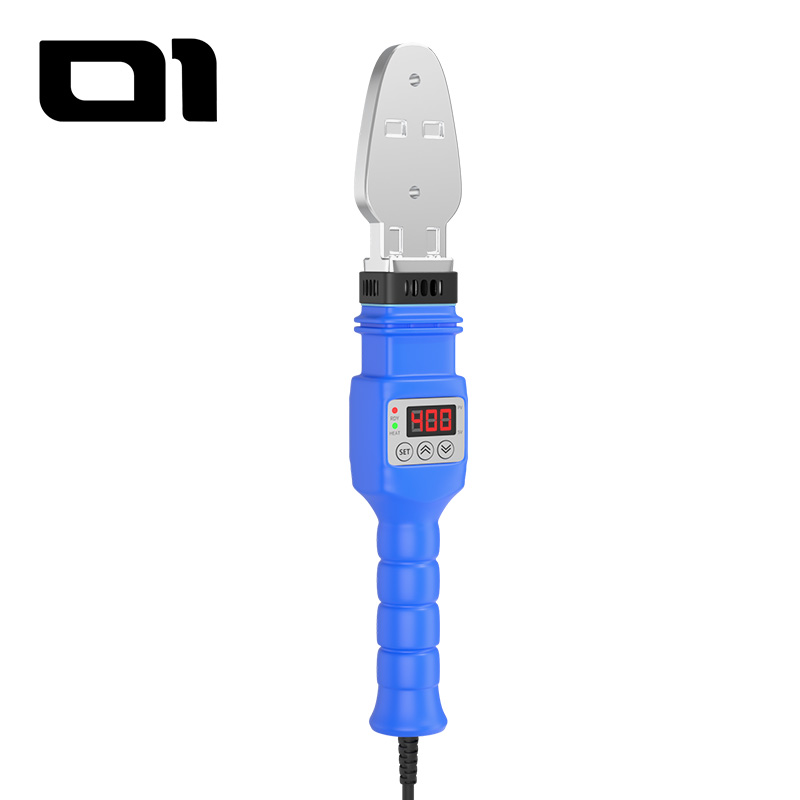
Understanding Fusion Welding
Fusion welding melts the pipe and fitting surfaces for a seamless connection. It is simpler and more portable, making it suitable for various environments, especially residential and commercial settings.
Temperature control is vital to avoid overheating or underheating. Fusion welding is well-suited for smaller pipes and allows adaptable piping arrangements. Equipment varies from manual to automatic, with digital controls in advanced models. Regular maintenance and safety practices are essential.
Key features of fusion welding:
- Simple and efficient
- Portable and user-friendly
- Requires temperature precision
- Best for smaller diameters
- Varies in equipment complexity
Advantages of Fusion Welding
Fusion welding creates leak-free joints adaptable to various pipe sizes and configurations. The equipment is affordable, portable, and user-friendly, reducing installation errors. Proper execution leads to durable results and lower maintenance costs.
Limitations of Fusion Welding
Surface preparation must be meticulous. Temperature control requires continuous monitoring, and the method is less effective for large diameters. These demands emphasize the need for skilled operation.
Comparing Butt and Fusion Welding
Butt welding excels with large pipes and high-pressure systems, offering strong joints for industrial use. Fusion welding is better for smaller projects, offering ease of use, quick setup, and adaptability.
Butt welding requires more skill and time; fusion welding is faster and simpler. Cost-wise, butt welding involves higher initial investment and specialized labor, while fusion equipment is more affordable and beginner-friendly.
Selecting the Right Welding Machine
Choose based on pipe diameter, project complexity, and environment. Butt welding machines handle large diameters and industrial conditions, while fusion machines are portable and suitable for small pipes and simple projects.
Consider initial cost, long-term value, and features like digital controls. Evaluate maintenance needs and technical support. User reviews and expert recommendations can guide the decision.
Conclusion
Butt welding machines are ideal for large-scale, high-pressure applications but require expertise and investment. Fusion welding machines offer practicality, portability, and ease of use for smaller projects. Understanding project requirements ensures the right choice, promoting efficiency and success in PPR pipe welding.